An Elemental Guide to Corrugated Boxes Manufacturer

Corrugated boxes are versatile packaging solutions widely used in various industries for shipping, storage, and protection of goods. This comprehensive guide explores the elemental aspects of corrugated boxes manufacturing, covering everything from raw materials and box design to production processes and quality control. By understanding these key components, readers will gain valuable insights into the world of corrugated box manufacturing and be better equipped to make informed decisions about their packaging needs.
Overview of Corrugated Boxes

Corrugated boxes, also known as cardboard boxes, are widely used for packaging, shipping, and storage purposes. They are made from corrugated fiberboard, which consists of linerboard and medium sandwiched between two flat layers. The unique structure of corrugated fiberboard provides strength, durability, and cushioning properties to the boxes.
Importance of Corrugated Boxes in Packaging
Corrugated boxes play a vital role in protecting goods during transportation and storage. They provide a lightweight yet sturdy packaging solution that can withstand stacking, impacts, and compression. Additionally, corrugated boxes are customizable, cost-effective, and recyclable, making them an environmentally friendly choice for packaging needs.
3 Purpose of the Guide
The purpose of this guide is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the elemental aspects of corrugated box manufacturing. By exploring the raw materials, box design considerations, production processes, quality control measures, environmental considerations, and emerging trends, readers will gain valuable insights into the world of corrugated box manufacturing and be better equipped to make informed decisions about their packaging needs.
Raw Materials for Corrugated Boxes

Paperboard
Paperboard is a primary raw material used in corrugated box manufacturing. It is a thick, stiff paper with high structural integrity. Different grades of paperboard are used for the linerboard (outer layers) and medium (fluted layer) of the corrugated fiberboard.
Linerboard
Linerboard is a flat, smooth, and strong paperboard used for the outer layers of the corrugated box. It provides the box with stiffness, printing surface, and protection against moisture and external elements.
Medium
The medium is a fluted paperboard layer that is sandwiched between the linerboards. It provides the box with structural strength, cushioning, and resistance to compression. The flutes in the medium also enhance the box’s insulation properties.
Adhesives
Adhesives are essential for bonding the layers of corrugated fiberboard together. Starch-based adhesives, commonly derived from corn or wheat, are widely used in box manufacturing due to their biodegradability and non-toxic nature.
Inks and Coatings
Inks and coatings are used for printing graphics, branding, and enhancing the visual appeal of corrugated boxes. Water-based inks and coatings are typically used due to their eco-friendly nature.
Corrugated Box Design
Box Styles and Types
Corrugated boxes come in various styles and types to accommodate different packaging needs. Common box styles include regular slotted containers (RSC), half-slotted containers (HSC), die-cut boxes, telescopic boxes, and many more. Each style offers specific features and benefits suited for particular applications.
Size and Dimension Considerations
The size and dimensions of a corrugated box are crucial in ensuring optimal packaging efficiency. Factors like product size, weight, fragility, and stacking requirements need to be considered when determining the appropriate box dimensions to provide adequate protection and space utilization.
Flute Types and Applications
Flutes are the S-shaped waves in the medium of corrugated fiberboard. Different flute profiles, such as A, B, C, E, and F, offer varying levels of cushioning, stacking strength, and insulation properties. Selecting the right flute type depends on the specific packaging requirements.
Printing and Graphics
Printing on corrugated boxes serves functional and aesthetic purposes. Various printing methods, such as flexography, lithography, and digital printing, are employed to apply branding elements, product information, barcodes, and other graphics.
Structural Design and Strength
The structural design of a corrugated box influences its strength, stacking ability, and protection capabilities. Design considerations include flaps, closures, reinforcements, partitions, and inserts. Advanced design software and engineering principles aid in optimizing the structural integrity of corrugated boxes.
Corrugated Box Manufacturing Process
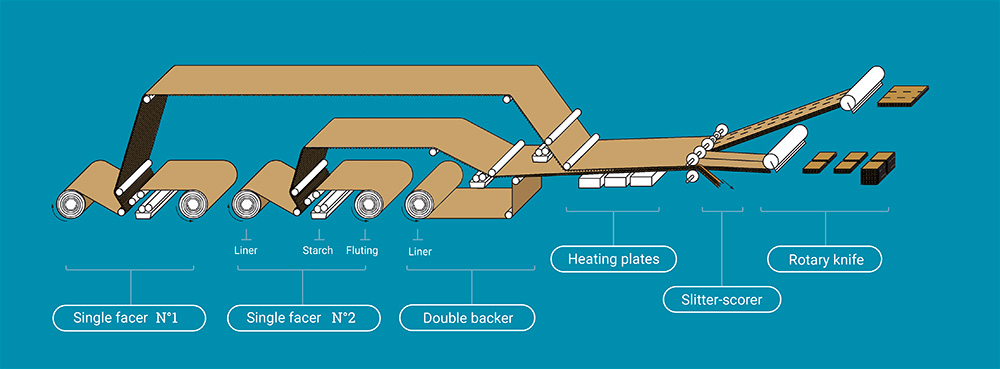
Stock Preparation
The stock preparation stage involves preparing the raw materials for the corrugated fiberboard production. It includes processes like pulping, cleaning, refining, and blending to achieve the desired paperboard properties.
Corrugating
Corrugating is the process of forming the fluted layer of the corrugated fiberboard. The medium is fed through heated corrugating rolls, which impart the desired flute profile. The corrugated medium is then bonded with linerboards using adhesives to create the corrugated fiberboard.
Gluing
In the gluing process, the linerboards and the medium are bonded together using starch-based adhesives. The adhesive is applied to the tips of the flutes, and the layers are brought together under pressure to form a strong bond.
Cutting and Creasing
Cutting and creasing machines are used to convert the corrugated fiberboard into flat sheets of specific dimensions. The cutting process involves cutting the sheets to the required size, while the creasing process creates score lines to facilitate folding and forming of the boxes.
Printing and Die Cutting
Printing machines apply inks and coatings to the flat sheets to create desired graphics and branding elements. Die-cutting machines then cut out the box shape from the printed sheets, creating the individual box blanks.
Folding and Gluing
The die-cut box blanks are folded and glued using specialized folding and gluing machines. The machines fold and align the flaps of the box, while applying adhesive to create a secure and sealed box structure.
Bundling and Shipping
Once the boxes are formed and glued, they are bundled into stacks and prepared for shipping. Proper bundling and stacking techniques ensure safe transportation to the end-users or storage facilities.
Quality Control in Corrugated Box Manufacturing
Raw Material Inspection
Raw material inspection involves verifying the quality and specifications of the paperboard, linerboard, medium, adhesives, and inks. This step ensures that the materials meet the required standards and are suitable for box manufacturing.
Process Control
Process control measures monitor various stages of the manufacturing process, including corrugating, gluing, cutting, printing, and folding. Regular inspections, testing, and adjustments are performed to maintain consistent quality and adherence to specifications.
Finished Product Testing
Finished product testing involves assessing the quality, strength, and performance of the manufactured corrugated boxes. Testing methods include burst strength, edge crush test, drop test, compression test, and humidity resistance testing.
Standards and Certifications
Corrugated box manufacturers often adhere to industry standards and certifications, such as International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards, Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification, and Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI) certification. These certifications ensure compliance with environmental and quality management systems.
Environmental Considerations

Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Corrugated boxes are inherently sustainable due to their recyclability, biodegradability, and renewable raw materials. Manufacturers and consumers are increasingly opting for sustainable packaging solutions, leading to innovations like lightweighting, eco-friendly inks, and bio-based adhesives.
Recycling and Waste Management
Corrugated boxes have a high recycling rate and can be recycled into new paper products. Recycling initiatives, such as collection programs and partnerships with recycling facilities, promote the circular economy and minimize waste.
Life Cycle Assessment
Life cycle assessment (LCA) evaluates the environmental impact of corrugated boxes throughout their entire life cycle. It considers factors like raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, transportation, use, and end-of-life treatment. LCA helps identify opportunities for environmental improvements and sustainable practices.
Advanced Techniques and Innovations

Digital Printing
Digital printing technology enables high-quality, on-demand printing of corrugated boxes. It allows for customization, shorter lead times, reduced waste, and cost-effective production of small batch sizes.
Customization and Personalization
Advancements in printing and cutting technologies enable manufacturers to offer customized and personalized corrugated boxes. Variable data printing, unique designs, and tailored packaging solutions cater to specific customer requirements and enhance branding opportunities.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics have revolutionized corrugated box manufacturing. Automated machinery improves production efficiency, accuracy, and consistency while reducing labor costs. Robots are increasingly used for tasks like material handling, gluing, stacking, and quality control.
Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things (IoT) in Box Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT sensors, data analytics, and machine learning, are transforming the manufacturing process. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and intelligent process optimization enhance productivity, quality control, and overall operational efficiency.
Market Trends and Outlook
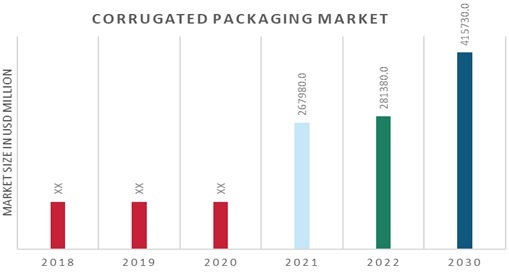
Global Corrugated Boxes Market
The global corrugated boxes market is witnessing steady growth, driven by increasing e-commerce activities, demand for sustainable packaging, and rising consumer expectations for product protection. Emerging markets, technological advancements, and industry collaborations are shaping the future of the market.
Emerging Technologies and Materials
Technological advancements continue to introduce new materials and manufacturing techniques to the corrugated box industry. Innovations like nanotechnology, bio-based materials, water-based coatings, and compostable adhesives offer promising alternatives for enhanced performance and sustainability.
E-commerce Packaging
The rapid growth of e-commerce has created a surge in demand for customized packaging solutions. Corrugated boxes play a crucial role in e-commerce packaging, providing protection during shipping, easy handling, and improved customer experiences.
Conclusion
This elemental guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the corrugated box manufacturing process. By understanding the raw materials, box design considerations, production processes, quality control measures, and environmental aspects, readers are equipped with valuable insights into the world of corrugated box manufacturing. As packaging needs continue to evolve, staying updated with emerging trends and technologies is essential for manufacturers to meet customer demands and contribute to a sustainable future.






Leave a Comment