Table of Contents
Toggle“Corrugated Box Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Guide Explained”
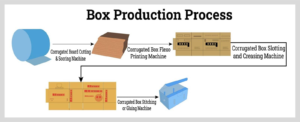
Complete Guide to the Corrugated Box Manufacturing Process
Corrugated boxes are the backbone of the packaging industry. Known for their strength, durability, and versatility, these boxes are widely used across retail, shipping, and storage sectors. Whether you’re a packaging professional or simply curious about how boxes are made, this guide explores the corrugated box manufacturing process in detail—from design to final shipment.
What Is a Corrugated Box?
A corrugated box is a container made from corrugated board—a material consisting of three layers: an inside liner, an outside liner, and a fluted corrugated medium sandwiched between them. This structure provides exceptional strength, making the box resistant to pressure, impact, and temperature fluctuations.
Corrugated boxes come in various forms such as Regular Slotted Containers (RSC), Half Slotted Containers (HSC), and die-cut boxes. They are widely used due to their eco-friendly, lightweight, and cost-effective nature.
Benefits of Corrugated Boxes in Packaging
- Lightweight & Durable: Easy to handle, yet strong enough to protect goods.
- Sustainable: Often made from recycled paper, promoting environmental responsibility.
- Versatile: Suitable for multiple industries, including e-commerce, food, electronics, and more.
- Customizable: Compatible with printing, folding, laminating, and die cutting processes for branding and product differentiation.
Corrugated Box Manufacturing Process Step by Step
Let’s break down the corrugated box manufacturing process step by step, highlighting the machinery, techniques, and key decisions involved.
- Design and Planning
Every corrugated box starts with a purpose. During this phase:
- Determine the box’s size, weight capacity, and use case.
- Choose the right type of corrugated sheet (single-wall, double-wall, or triple-wall).
- Consider printability, durability, and cost when selecting materials.
- Plan structural design using CAD software or manual templates.
This stage plays a critical role in how boxes are made effectively and efficiently.
- Material Preparation
Prepare the raw materials used in the manufacturing of corrugated boxes:
- Paper reels are sourced for liners and the fluted medium.
- Adhesives are readied for bonding the layers.
- Paper is conditioned for humidity to maintain optimal flexibility and strength.
- Corrugation (Fluting Process)
This is the core step in the corrugation process:
- Paper medium is passed through heated corrugating rollers.
- It forms flutes (waves) that are then glued between the inner and outer liners.
- This structure gives the corrugated box its strength and cushioning ability.
Specialized box machines automate and control this phase for consistency and efficiency.
- Cutting and Creasing
Now, the corrugated board is cut and creased using precision equipment:
- Slotters and die cutting machines create specific shapes and folding lines.
- Boxes may have flaps, tabs, or windows depending on the product needs.
- Folding carton styles are shaped during this process.
Accurate creasing ensures smooth folding and forming in later steps.
- Printing and Branding (Optional)
Branding is a vital part of the corrugated box manufacturing process:
- Box printing uses flexographic or digital methods to apply logos, instructions, or barcodes.
- Special coatings or laminating can enhance visual appeal and surface durability.
- This adds value for retail packaging and customer experience.
- Folding and Gluing
This step transforms flat boards into box shapes:
- Machines fold the creased panels and apply adhesive to appropriate areas.
- Glue types vary depending on box usage—water-based for food-grade, or hot-melt for heavy-duty.
Once dried, the structure becomes rigid and ready for filling.
- Quality Control and Inspection
Quality assurance ensures consistency across production:
- Inspect boxes for misalignment, incomplete gluing, or size defects.
- Evaluate structural integrity and box printing clarity.
- Regular testing prevents issues during shipping and handling.
- Packaging and Shipping
Once approved, boxes are stacked and packed:
- Bundled boxes are stored for distribution or delivered directly to clients.
- Labels and handling instructions are added for safety during transit.
- Companies may use box machines for automated stacking and wrapping.
- Recycling and Sustainability
An essential part of the carton box manufacturing process is sustainability:
- Used boxes are recycled into new paper products.
- Waste material is minimized through optimized die-cutting and folding carton designs.
- Many manufacturers adopt circular economy practices to reduce environmental impact.
How to Make Corrugated Boxes: Key Takeaways
Whether you’re starting a packaging business or just exploring the process, here’s a summary of how to make corrugated boxes:
- Start with the purpose and design.
- Choose high-quality materials.
- Use automated machines for cutting, corrugation, and die cutting.
- Add custom branding with box printing.
- Inspect each batch for consistency and durability.
- Promote recycling and eco-conscious practices.
The Future of Corrugated Box Manufacturing
The corrugated box manufacturing process continues to evolve with advancements in automation, sustainable materials, and smart packaging technologies. As demand for e-commerce and global shipping rises, so does the need for strong, lightweight, and recyclable packaging solutions. Understanding the corrugated box making process is key to producing high-quality packaging that meets modern demands while staying eco-friendly.




Leave a Comment