“Understanding the Corrugated Box Production Process: An Overview”
A corrugated box, commonly known as a cardboard box, is a versatile packaging solution widely used for shipping, storage, and retail purposes. It is constructed from layers of paperboard, typically consisting of three main components: an inner liner, an outer liner, and a corrugated medium sandwiched between them.
The corrugated medium, made of fluted paper, gives the box its distinctive strength and rigidity. It adds structural integrity while also providing insulation against shocks, impacts, and temperature changes. The outer and inner liners provide smooth surfaces for printing branding, labeling, and handling instructions.
Corrugated boxes come in various types and sizes, each designed for specific applications. These include regular slotted containers (RSC), half-slotted containers (HSC), and more specialized designs like die-cut boxes for unique products.
The benefits of corrugated boxes include their lightweight nature, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendliness, as they are often made from recycled materials. Their assembly is user-friendly, often requiring minimal adhesive or tape. Additionally, the corrugated structure allows for stacking and easy handling during transportation.
“Step-by-Step Guide to the Creation of Corrugated Boxes”
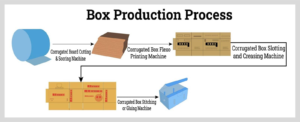
Creating corrugated boxes involves a systematic process to ensure their structural integrity and functionality. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the creation of corrugated boxes:
- Design and Planning:
- Determine the box’s purpose, dimensions, and intended contents.
- Choose the appropriate type of corrugated board, considering factors like strength, durability, and printability.
- Material Preparation:
- Obtain the necessary corrugated board sheets, inner and outer liners, and adhesives.
- Ensure the paperboard is properly stored to maintain its quality.
- Cutting and Creasing:
- Use specialized machinery to cut the corrugated board into appropriately sized panels for the box.
- Crease the panels at specific locations to facilitate folding and forming.
- Printing and Labeling (Optional):
- If desired, print branding, product information, or artwork onto the outer liner using flexographic or digital printing methods.
- Gluing and Laminating:
- Apply adhesive to the corrugated medium using rollers or sprayers.
- Attach the inner and outer liners to the corrugated medium, creating a layered structure.
- Die-Cutting and Slotting:
- For specialized box designs, use a die-cutting machine to create precise cuts and perforations.
- Slotting machines create the necessary flaps and tabs for folding.
- Folding and Forming:
- Fold the corrugated board along the creases to create the box’s basic shape.
- Ensure accurate alignment of flaps and edges for a neat appearance.
- Gluing and Closure:
- Apply adhesive to the appropriate flaps and tabs to secure the box’s structure.
- Ensure proper sealing to prevent the box from coming apart during handling and shipping.
- Quality Control:
- Inspect the completed boxes for any defects, misalignments, or glue irregularities.
- Check dimensions, print quality, and structural integrity.
- Packaging and Shipping:
- Once approved, stack the completed boxes in a safe and organized manner for storage or distribution.
- Ensure the boxes are properly labeled and protected to prevent damage during shipping.
- Recycling and Sustainability:
- Encourage the recycling of corrugated boxes to contribute to environmental sustainability.
- Properly dispose of any waste materials generated during the box creation process.




Leave a Comment