How do you ensure the recyclability and sustainability of your packaging solutions?

Ensuring the recyclability and sustainability of packaging solutions is crucial in today’s world, where environmental concerns and the need for sustainable practices are gaining increasing importance. Packaging plays a significant role in the lifecycle of products, from production to consumption and disposal, and has a substantial impact on the environment. To address these concerns, companies are adopting various strategies and approaches to make their packaging solutions more recyclable and sustainable. In this response, I will discuss some of the key measures and considerations for achieving recyclability and sustainability in packaging.
Material Selection
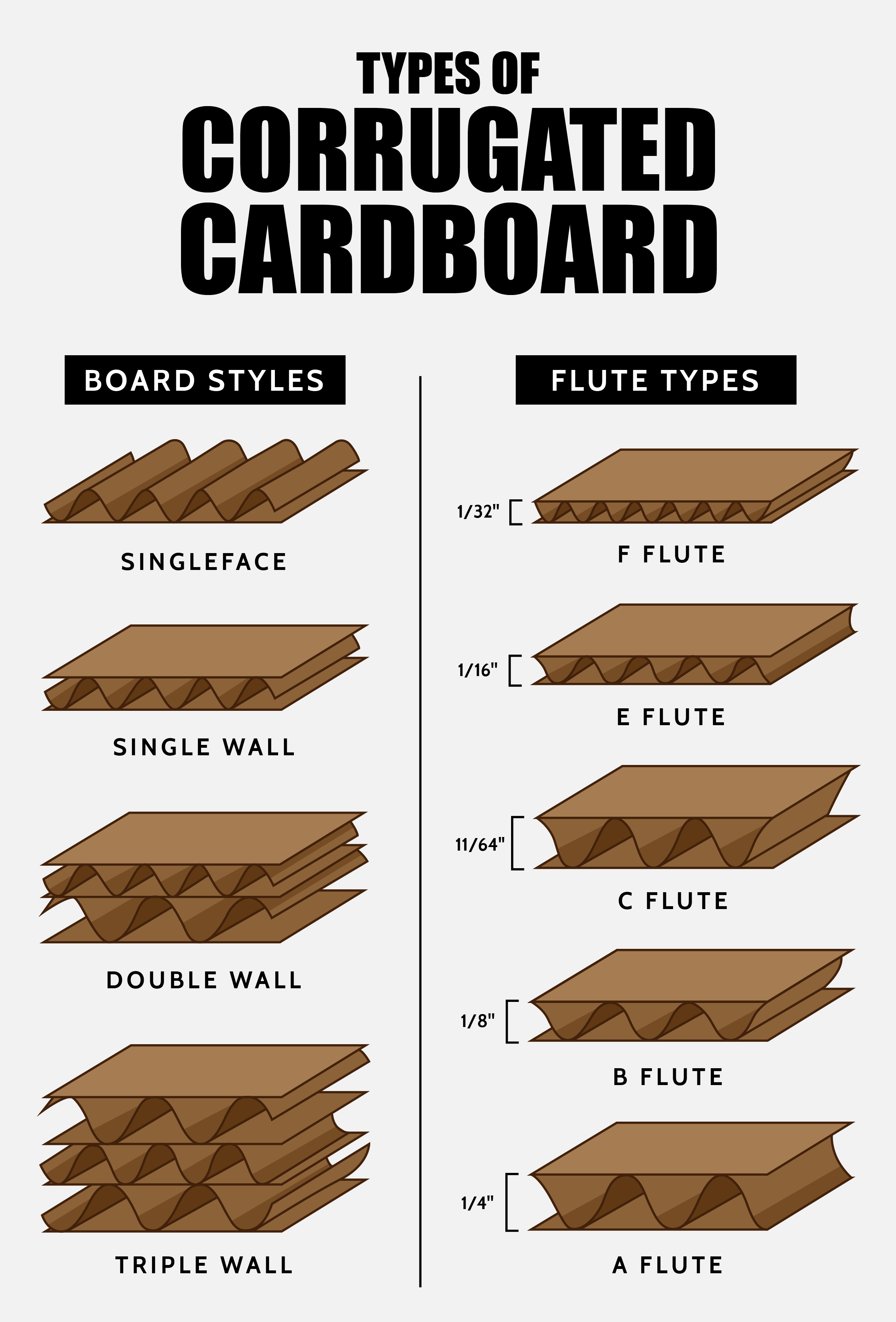
One of the fundamental aspects of creating recyclable and sustainable packaging is choosing the right materials. Packaging materials should be selected based on their environmental impact, recyclability, and availability of recycling infrastructure. Some key considerations include:
- Renewable and Biodegradable Materials: Opting for renewable and biodegradable materials, such as paperboard, cardboard, bioplastics, and compostable materials, can significantly reduce the environmental impact of packaging. These materials can be derived from renewable sources and can decompose naturally, minimizing their contribution to waste streams.
- Recyclable Materials: Choosing packaging materials that are widely accepted in recycling systems helps ensure that they can be effectively recycled. Common recyclable materials include glass, aluminum, steel, and certain types of plastics (e.g., PET, HDPE).
- Lightweight Materials: Using lightweight materials reduces the overall environmental footprint of packaging. It reduces energy consumption in transportation and requires fewer resources for production. However, it is important to strike a balance between lightweighting and maintaining the necessary strength and protection for the packaged product.
- Avoiding Hazardous Materials: Packaging should not contain harmful substances that can leach into the environment or pose a risk during recycling. Materials such as heavy metals, certain plastics (e.g., PVC), or toxic coatings should be avoided.
Design for Recycling
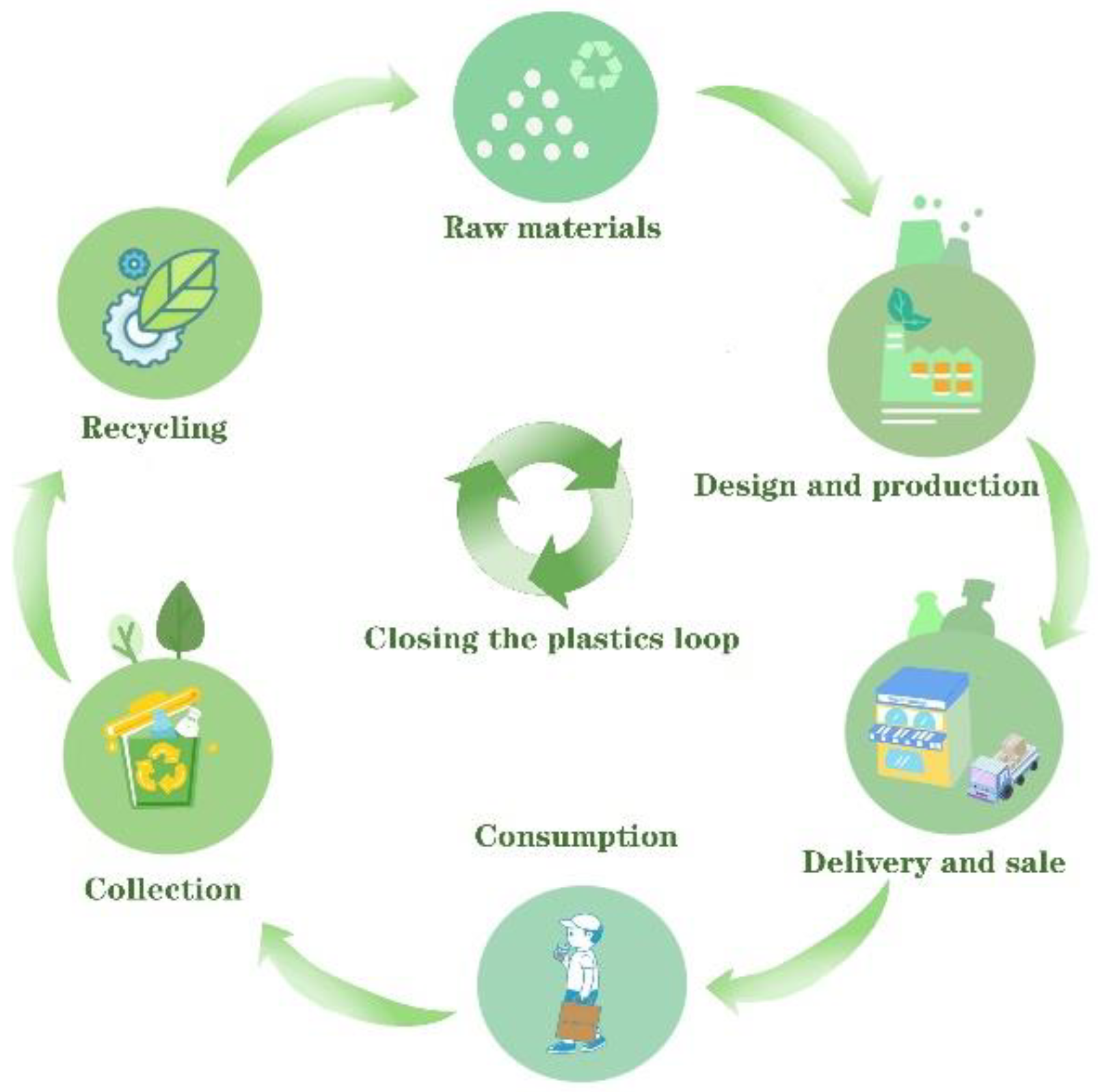
Designing packaging with recycling in mind is essential for optimizing the recycling process and maximizing the recovery of materials. Some key design considerations include:
- Single Material Packaging: Packaging that is made from a single material is typically easier to recycle compared to complex multi-layered structures. Single-material packaging allows for efficient separation and processing during recycling.
- Separable Components: Designing packaging with separable components makes it easier to dismantle and recycle. For example, using detachable caps or separating plastic components from paper or cardboard packaging simplifies the recycling process.
- Clear Labeling: Providing clear and standardized labeling on packaging can guide consumers on how to properly dispose of the packaging after use. Labeling should indicate the material type and appropriate recycling instructions, including information on whether it is recyclable, compostable, or needs special handling.
- Minimizing Non-Recyclable Components: Packaging should be designed to minimize the use of non-recyclable components, such as laminates, mixed materials, or complex additives that hinder the recycling process.
- Compatibility with Recycling Infrastructure: Packaging design should consider the existing recycling infrastructure and ensure compatibility with sorting and processing technologies in place. Collaboration with recycling facilities can help optimize the design for recyclability.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)

Implementing Extended Producer Responsibility programs can incentivize packaging sustainability by holding producers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including packaging waste. Key aspects of EPR programs include:
- Packaging Waste Reduction Targets: Setting targets for packaging waste reduction encourages companies to adopt sustainable packaging practices. Targets can be based on metrics such as weight, material composition, or recycling rates.
- Recycling Infrastructure Investment: Producers can contribute to the development and improvement of recycling infrastructure, making it more accessible and efficient. Collaborating with local authorities, waste management facilities, and recyclers can help improve recycling rates and reduce waste.
- Take-Back Schemes: Implementing take-back schemes, where producers collect and recycle their packaging after use, promotes the circularity of packaging materials. Producers can partner with retailers or establish collection points to ensure proper recovery and recycling of packaging waste.
Innovative Packaging Solutions

Advancements in technology and innovation offer opportunities to develop new packaging solutions that are both sustainable and functional. Some examples include:
- Biodegradable and Compostable Packaging: Biodegradable packaging materials, such as bio-based plastics or plant-based films, can break down naturally in composting systems. Compostable packaging can be an eco-friendly alternative for certain applications, especially in food service and agriculture.
- Recyclable Flexible Packaging: Flexible packaging, commonly used for snacks and pouches, presents recycling challenges due to its multi-layered structure. However, advances in recycling technologies, such as specialized sorting and processing methods, are enabling the recycling of flexible packaging.
- Plant-based and Bio-Based Plastics: Plant-based plastics, derived from renewable sources like corn or sugarcane, can be a sustainable alternative to conventional plastics. These bio-based plastics have the potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
- Smart Packaging: Integration of smart technologies, such as RFID tags or sensors, can help optimize packaging use, reduce waste, and enhance supply chain efficiency. For example, smart packaging can provide real-time information on product freshness or facilitate inventory management, leading to better resource utilization.
Collaboration and Industry Initiatives

Addressing the challenges of packaging sustainability requires collaboration among stakeholders across the value chain. Industry initiatives and partnerships can drive collective action towards sustainable packaging. Some examples include:
- Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs): Collaborating with MRFs and recyclers can help identify packaging design opportunities and ensure the compatibility of packaging materials with existing recycling infrastructure.
- Recycling Education and Awareness Programs: Companies can invest in educational programs to raise awareness among consumers about the importance of recycling and proper disposal of packaging. These programs can encourage behavior change and promote a culture of recycling.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Participating in circular economy initiatives, such as the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s New Plastics Economy, can provide guidance and resources for transitioning towards more sustainable packaging models. These initiatives promote a holistic approach to packaging design, use, and recovery.
- Certification and Standards: Adhering to recognized certification and standards, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for sustainably sourced paper or the Sustainable Packaging Coalition’s How2Recycle label, can provide credibility and transparency to packaging sustainability efforts.
Life Cycle Assessments (LCA)
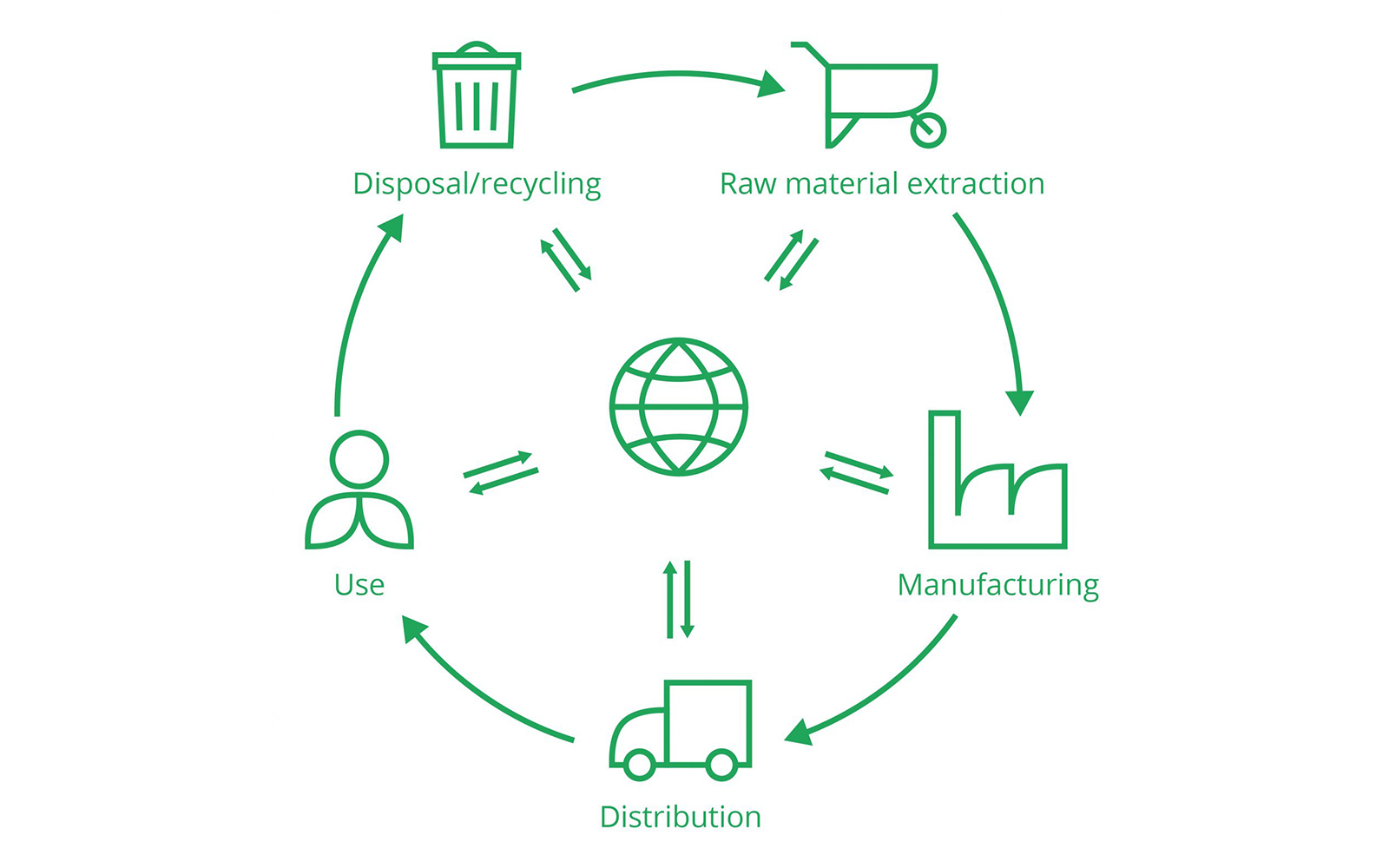
Conducting life cycle assessments helps evaluate the environmental impact of packaging solutions throughout their entire lifecycle. LCAs provide insights into the energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion associated with packaging. By identifying hotspots and areas for improvement, companies can make informed decisions to enhance the sustainability of their packaging.
Consumer Engagement

Engaging consumers in sustainable packaging practices is crucial for driving behavior change and increasing recycling rates. Companies can undertake various initiatives to promote consumer participation:
- Clear Communication: Providing clear and concise information on packaging labels about recycling instructions, environmental benefits, and the importance of recycling encourages consumers to take appropriate actions.
- Incentives and Rewards: Offering incentives or rewards for recycling packaging, such as loyalty points or discounts, can motivate consumers to participate actively in recycling programs.
- Consumer Education: Educating consumers through campaigns, social media, or product information can raise awareness about sustainable packaging practices and the positive environmental impact of recycling.
In conclusion, ensuring the recyclability and sustainability of packaging solutions requires a multi-faceted approach involving material selection, design optimization, extended producer responsibility, innovation, collaboration, and consumer engagement. By adopting these strategies, companies can reduce the environmental footprint of their packaging, promote recycling, and contribute to a more sustainable future.




Leave a Comment